Captive insurance, often referred to as a hidden gem in the world of risk management, holds immense potential for businesses looking to take control of their insurance needs. With the ability to not only protect against risks, but also provide financial advantages, captive insurance has become a popular choice for savvy businesses. One particular type of captive insurance gaining significant attention is the 831(b) captive.
The 831(b) captive, named after the corresponding section of the IRS tax code, offers small to medium-sized businesses a tax advantage that can greatly impact their bottom line. This captive insurance arrangement allows businesses to create their own insurance company, tailored specifically to their unique risks and challenges. By doing so, businesses can better manage these risks, while potentially enjoying substantial tax benefits.
The IRS 831(b) tax code provides certain tax exemptions for microcaptives, making it an attractive option for businesses seeking more control over their insurance costs. Under this code, qualifying captive insurance companies with annual premiums of $2.3 million or less are taxed at a significantly reduced rate, allowing businesses to retain more of their hard-earned revenue.
In the competitive business landscape, where risks seem to lurk around every corner, captive insurance offers a refreshing alternative to traditional insurance arrangements. By embracing the power of captives, businesses can take charge of their risk management strategies, protect their assets, and potentially unlock new avenues of financial growth.
As we delve deeper into the world of captive insurance, let us explore the benefits, intricacies, and potential pitfalls that businesses must consider before embarking on this risk management journey. Let us discover together how unleashing the power of captive insurance can empower businesses to navigate uncertain terrain and steer towards a more secure and prosperous future.
Understanding Captive Insurance
Captive insurance is a powerful tool that businesses can utilize for effective risk management. With the help of captive insurance, companies can gain greater control over their insurance programs by creating their own insurance company. This alternative risk management strategy allows businesses to assume the risks associated with their operations while also reaping the benefits of reduced premiums and increased risk coverage.
At the heart of captive insurance is the IRS 831(b) tax code, which provides certain tax advantages for small insurance companies. These tax advantages enable businesses to set up small captives, known as microcaptives, and enjoy tax benefits such as tax-exempt status for premiums received. By taking advantage of the IRS 831(b) tax code, businesses can not only mitigate risk but also potentially save on taxes, making captive insurance a compelling option.
Captive Insurance
Captive insurance fundamentally empowers businesses to tailor their insurance programs to their specific needs. By customizing coverage options and terms, companies can address the unique risks they face, while avoiding the limitations and costs imposed by traditional insurance providers. With captive insurance, businesses enhance their risk management abilities, gain financial flexibility, and ultimately unlock the power to protect themselves from unforeseen events.
The Benefits of Utilizing 831(b) Captive Insurance
Captive insurance, specifically under the IRS 831(b) tax code, offers several notable advantages for businesses seeking effective risk management strategies. This innovative form of self-insurance enables companies to take control and directly address their unique and specific risks, resulting in greater financial stability and enhanced protection.
Firstly, one key benefit of captive insurance lies in its cost-saving potential. By establishing their own insurance company, businesses can bypass the traditional insurance market and its associated costs, such as broker commissions and profit margins. This allows companies to retain more of their premiums and allocate funds more efficiently towards managing their risks.
Moreover, captive insurance provides businesses with enhanced coverage flexibility. Unlike traditional insurance policies, captive insurance enables companies to tailor their coverage to align precisely with their risk profile. With the ability to customize policy terms and conditions, businesses can ensure that their unique risks are adequately addressed, maximizing the effectiveness of their insurance coverage.
Additionally, captive insurance offers remarkable tax advantages. Under IRS 831(b) tax code, small insurance companies with annual premiums not exceeding $2.3 million can elect to be taxed only on their investment income. This favorable tax treatment can result in substantial tax savings for businesses, freeing up funds that can be reinvested for growth or utilized for further risk management measures.
In summary, engaging in captive insurance, particularly through the utilization of the IRS 831(b) tax code, can empower businesses in various ways. From cost savings and coverage flexibility to significant tax benefits, captive insurance provides businesses with a powerful tool for effectively managing their risks and securing their financial future.
Navigating the IRS 831(b) Tax Code and Microcaptive Requirements
When it comes to utilizing captive insurance for risk management, understanding the intricacies of the IRS 831(b) tax code and meeting the requirements for microcaptives is crucial. The IRS 831(b) tax code specifically pertains to small and closely-held insurance companies, allowing them certain tax advantages.
To qualify for the benefits provided by the IRS 831(b) tax code, businesses must ensure they meet certain requirements. Firstly, the company must be an insurance company that is owned by its shareholders and primarily operates to provide insurance coverage for specific risks. These requirements often align with the objectives of captive insurance, making it an attractive option for businesses looking to manage risk effectively.
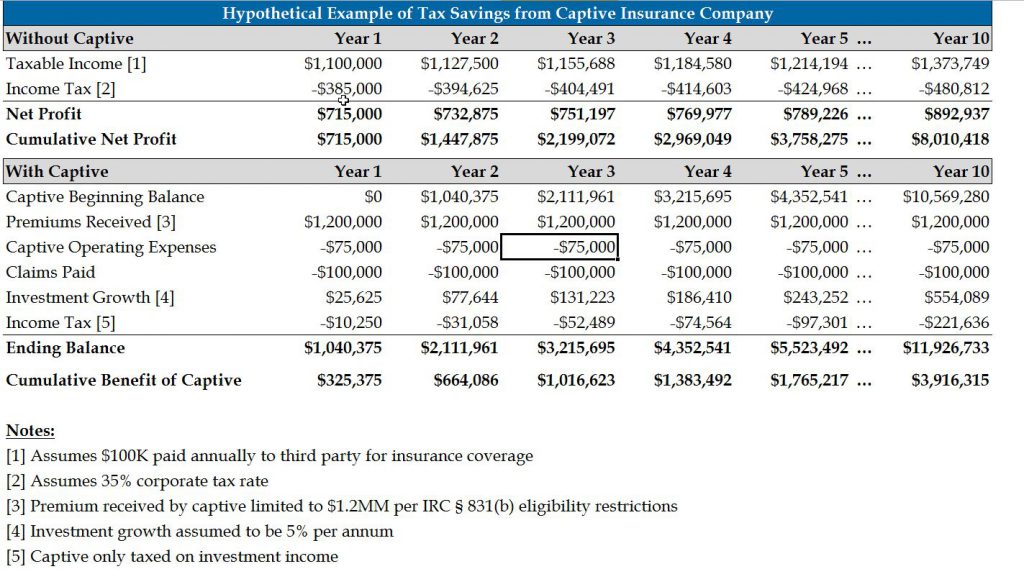
Additionally, the insurance premiums collected by the microcaptive must not exceed $2.3 million in a year. This limit ensures that the tax advantages provided by the IRS 831(b) tax code are targeted towards smaller entities. By adhering to this requirement, businesses can leverage the benefits of captive insurance while enjoying the potential tax advantages granted by the IRS.
In order to navigate the IRS 831(b) tax code successfully, it is essential for businesses considering captive insurance to have a thorough understanding of the regulations and guidelines. By partnering with experienced professionals in the field, companies can ensure compliance with the tax code and maximize the advantages of microcaptives for their risk management strategies. Properly navigating the IRS 831(b) tax code and meeting the microcaptive requirements enables businesses to unlock the power of captive insurance for effective risk management.
